Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; National Institutes of Natural Sciences*
JAEA-Review 2022-059, 34 Pages, 2023/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of the continuous monitoring of tritium water by mid-infrared laser spectroscopy" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to demonstrate the principle of short-time measurement of tritiated water at the "60 Bq/cc level" using a cavity ring-down measurement system with a mid-infrared laser. In order to achieve the above goal, (1) research on the cavity ring-down system and (2) evaluation of hydrogen isotope composition under environmental conditions and preparation of standard samples (subcontractor: Hirosaki University) were conducted this fiscal year. In (1), a mid-infrared cavity ring-down test was conducted. An optical bench (3 m  1.2 m) was set up in the laboratory, …
1.2 m) was set up in the laboratory, …
Furusawa, Akinori; Takenaka, Yusuke; Nishimura, Akihiko
Applied Sciences (Internet), 9(17), p.3544_1 - 3544_12, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:60.45(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Remote-controlled, non-destructive testing is necessary to detect corrosion of the reinforced concrete structures at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (NPP) de-commissioning site. This work aims to demonstrate that laser-induced ultrasonic guided wave technology can be applied to achieve this task. Hence, accelerated electrolytic corrosion is performed on a reinforced concrete specimen fabricated by embedding a steel rod into mortar. Waveforms of the laser-induced ultrasonic guided wave on the rod are measured with a previously employed piezoelectric transducer (PZT) probe, for each fixed corrosion time. Based on the results of Fourier and wavelet transforms of the waveforms, issues concerning the detection and extent of rebar corrosion are discussed. It is exhibited that the changes in bonding strength due to corrosion are distinguishable in the frequency domain of the ultrasonic signal.
Muramatsu, Toshiharu; Aoyagi, Yuji*; Yoshiuji, Takahiro*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai 2017-Nendo Nenji Taikai Koen Rombunshu (DVD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2017/09
A general-purpose three-dimensional thermohydraulics numerical simulation code SPLICE was developed at Japan Atomic Energy Agency and designed to deal with gas-liquid-solid consolidated incompressible viscous flows with a phase change process in various laser applications, such as welding, coating, cutting, etc. The result obtained from metal powder laser additive manufacturing simulations is very encouraging in the sense that the SPLICE code would be used as one of efficient tools to provide the laser irradiation conditions.
Furusawa, Akinori; Nishimura, Akihiko; Takebe, Toshihiko*; Nakamura, Masaki*; Takenaka, Yusuke*; Saijo, Shingo*; Nakamoto, Hiroyuki*
E-Journal of Advanced Maintenance (Internet), 9(2), p.44 - 51, 2017/08
The aim of this work is to investigate the applicability of ultrasonic guided wave for evaluation of laser beam butt-welding quality. Ten in total test pipes having welding seam is prepared. Two piece of pipe are jointed and continuous laser beam is irradiated on the edges, varying laser irradiation power, welding side and surface profile of the adjacent edges of the pipe. Ultrasonic guided wave testing experiment is performed on the pipes. Torsional mode guided wave is excited by EMAT. The experimental results are analyzed and issues are discussed. The reflection wave bullet from the poor interface of the welding seam is clearly observed, whereas no reflection from fine welded line. From the aspect of laser irradiation power, welding side and surface profile of the adjacent edges, the relation between the interface condition and detection wave bullet are analyzed. It is found that the ultrasonic guided wave technologies have the potential for evaluating laser beam butt-welding seam.
Furusawa, Akinori; Nishimura, Akihiko; Takenaka, Yusuke*; Nakamura, Kaori*
Proceedings of 54th Annual Meeting of Hot Laboratories and Remote Handling (HOTLAB 2017) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2017/00
Testing of concrete structures in NPPs is needed to guarantee hereafter workability. Recent work says Core Concrete Reaction advances erosion of the concrete structures of Fukushima NPPs and it's difficult to estimate the correct depth of CCR. In addition, it is clear that seawater intrusion makes the rebar in the concrete structures corroded, thus, advanced remote testing methods for the deterioration should be considered. Gap or decrease of the adhesiveness between rebar and outer concrete appears in its deterioration process. We had a sense of possibility introducing a new testing method based on that. The concept is to propagate laser-excited ultrasonic gathering the information about the deterioration inside and received at distance with LDV. In this work, we investigate and report how it has the effect on propagating ultrasonic along the rebar to decrease adhesiveness between the rebar and the concrete experimentally.
 Se(
Se( , n) cross section and uncertainty evaluation of the
, n) cross section and uncertainty evaluation of the  Se(n,
Se(n,  ) cross section
) cross sectionKitatani, Fumito; Harada, Hideo; Goko, Shinji*; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Yamada, Kawakatsu*; Igashira, Masayuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(4), p.475 - 485, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:43.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)Seya, Michio; Kureta, Masatoshi; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Nakamura, Hironobu; Harada, Hideo; Hajima, Ryoichi
Proceedings of INMM 55th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2014/07
JAEA has been implementing development programs of basic technologies of the following advanced NDA (non-destructive assay) of nuclear material (NM) for nuclear safeguards and security. (1) Alternative to  He neutron detection using ZnS/B
He neutron detection using ZnS/B O
O ceramic scintillator, (2) NRD (neutron resonance densitometry) using NRTA (neutron resonance transmission analysis) and NRCA (neutron resonance capture analysis), (3) NRF (nuclear resonance fluorescence)-NDA using laser Compton scattered (LCS)
ceramic scintillator, (2) NRD (neutron resonance densitometry) using NRTA (neutron resonance transmission analysis) and NRCA (neutron resonance capture analysis), (3) NRF (nuclear resonance fluorescence)-NDA using laser Compton scattered (LCS)  -rays (intense mono-energetic
-rays (intense mono-energetic  -rays). The development program (1) is for NDA systems that use ZnS/B
-rays). The development program (1) is for NDA systems that use ZnS/B O
O ceramic scintillator as alternative neutron detector to
ceramic scintillator as alternative neutron detector to  He for coming shortage of its supply. The program (2) is for a NDA system of isotopic composition measurement (non-destructive mass spectroscopy) in targets such as particle-like melted fuel debris using NRTA and NRCA. The program (3) is for NDA systems using a specific NRF reaction of certain Pu/U isotope caused by mono-energetic LCS
He for coming shortage of its supply. The program (2) is for a NDA system of isotopic composition measurement (non-destructive mass spectroscopy) in targets such as particle-like melted fuel debris using NRTA and NRCA. The program (3) is for NDA systems using a specific NRF reaction of certain Pu/U isotope caused by mono-energetic LCS  -ray with energy tuned to the specific excited state of the isotope. This paper introduces above three programs.
-ray with energy tuned to the specific excited state of the isotope. This paper introduces above three programs.
Hatae, Takaki; Naito, Osamu; Kitamura, Shigeru; Sakuma, Takeshi*; Hamano, Takashi*; Nakatsuka, Masahiro*; Yoshida, Hidetsugu*
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 49, p.S160 - S164, 2006/12
no abstracts in English
Hatae, Takaki; Kondoh, Takashi; Naito, Osamu; Nakatsuka, Masahiro*; Yoshida, Hidetsugu*
Proceedings of 12th International Symposium on Laser-Aided Plasma Diagnostics (LAPD-12) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/09
no abstracts in English
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Kato, Masaaki; Wakaida, Ikuo; Watanabe, Kazuo
JAERI-Tech 2005-043, 27 Pages, 2005/08
Multi-step resonance ionization spectrometry for long-lived nuclei in nuclear waste materials requires laser sources having high frequency stability and tunability. In this study we have developed a novel frequency control system consisting of digital circuitry and computer to improve the frequency tunability of the developed laser stabilization system using dichroic atomic vapor laser lock (DAVLL) and fringe offset lock (FOL) techniques. Based on the heterodyne experiment and multi-step laser induced fluorescence spectroscopy of atomic Ca, the frequency stability and tunability of the developed system were evaluated.
Hatae, Takaki; Nakatsuka, Masahiro*; Yoshida, Hidetsugu*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 80(10), p.870 - 882, 2004/10
A high performance phase conjugate mirror by stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS-PCM) is applied to Thomson scattering diagnostics in JT-60U for the first time. To improve the measurement performance, two developments were performed with SBS-PCM. First, we developed a new optical design to provide a double-pass scattering scheme with SBS-PCM. A laser beam passing through the plasma is reflected by the SBS-PCM, and a reflected beam returned back through the same path as coming one by the phase conjugate effect, and passed through the plasma again. The double path Thomson scattering scheme demonstrated in JT-60U plasma that a factor of 1.6 increase of the scattered light in contrast with single-pass scattering. Second, an improvement of the output power of YAG laser system using the SBS-PCM was performed. As a result, average power was increased over 8 times in contrast with conventional system, and was achieved up to 368 W (7.4 J  50 Hz). A multi-pass Thomson scattering scheme is also proposed based on the results of double-pass scattering.
50 Hz). A multi-pass Thomson scattering scheme is also proposed based on the results of double-pass scattering.
Minehara, Eisuke
Proceedings of 28th Linear Accelerator Meeting in Japan, p.402 - 403, 2003/08
The JAERI superconducting RF linac-based free-electron laser has successfully generated 6% highly-efficient, a few hundreds of femtosecond, and several kW class high power FEL light several years ago. In the presentation, it will be reprted that the JAERI plans to develop the higher power free-electron lasers and their application to large-scale non-thermal precision manufacturing technology.
 -particle diagnostics by CO
-particle diagnostics by CO laser collective Thomson scattering in ITER
laser collective Thomson scattering in ITERKondoh, Takashi; Richards, R. K.*; Hutchinson, D. P.*; Sugie, Tatsuo; Costley, A. E.*; Miura, Yukitoshi; Lee, S.*
Proceedings of 30th EPS Conference on Controlled Fusion and Plasma Physics (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2003/07
In order to understand the behavior of alpha-particles which are the dominant heat source in a burning plasma, it is necessary to measure the spatial distribution of the number of the alpha-particles and their energy spectrum. A collective Thomson scattering (CTS) system based on a pulsed CO laser is being developed and is under consideration for alpha-particle measurements on ITER. Heating beam ions (E = 1 MeV) are normally co-injected and have a similar velocity with alpha-particles in ITER. The CTS measurement can not, in general, distinguish beam ions and alpha-particles which have the same velocity. A vertical scattering geometry to distinguish between beam ions and alpha-particles is proposed. Calculations have shown that the vertically viewing CTS can resolve counter-travelling alphas without being masked by beam ions. Preliminary design of a beam line and a receiver system with the vertical scattering geometry has been developed. A proof-of-principle test on the CTS system using the JT-60U plasma is being conducted.
laser is being developed and is under consideration for alpha-particle measurements on ITER. Heating beam ions (E = 1 MeV) are normally co-injected and have a similar velocity with alpha-particles in ITER. The CTS measurement can not, in general, distinguish beam ions and alpha-particles which have the same velocity. A vertical scattering geometry to distinguish between beam ions and alpha-particles is proposed. Calculations have shown that the vertically viewing CTS can resolve counter-travelling alphas without being masked by beam ions. Preliminary design of a beam line and a receiver system with the vertical scattering geometry has been developed. A proof-of-principle test on the CTS system using the JT-60U plasma is being conducted.
 laser for ion energy spectrum measurements in JT-60U
laser for ion energy spectrum measurements in JT-60UKondoh, Takashi; Miura, Yukitoshi; Lee, S.*; Richards, R. K.*; Hutchinson, D. P.*; Bennett, C. A.*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 74(3), p.1642 - 1645, 2003/03
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:68.13(Instruments & Instrumentation)Measurements of energy spectrum and density profile of confined alpha-particles are required for ITER. Several methods have been proposed, however, a measurement technique hasn't been established yet. A collective Thomson scattering (CTS) system based on a pulsed CO laser is being developed to demonstrate feasibility of alpha-particle diagnostics for ITER. The pulse laser (15J, 1
laser is being developed to demonstrate feasibility of alpha-particle diagnostics for ITER. The pulse laser (15J, 1 m, 0.6
m, 0.6  m) and a wide band (~ 8GHz) heterodyne receiver with a quantum-well infrared photodetector (QWIP) have been developed and installed in the JT-60U tokamak. Stray light is reduced by a notch filter with hot CO
m) and a wide band (~ 8GHz) heterodyne receiver with a quantum-well infrared photodetector (QWIP) have been developed and installed in the JT-60U tokamak. Stray light is reduced by a notch filter with hot CO gas. Heterodyne receiver is absolutely calibrated using large area blackbody radiation source. Scattered signal from JT-60U plasma has not detected because of electrical noise originated from discharge of the pulsed laser and stray signal caused by impurity of the spectrum of the pulsed laser.
gas. Heterodyne receiver is absolutely calibrated using large area blackbody radiation source. Scattered signal from JT-60U plasma has not detected because of electrical noise originated from discharge of the pulsed laser and stray signal caused by impurity of the spectrum of the pulsed laser.
Isozaki, Futoshi*; Kikuchi, Taiji; Ioka, Ikuo; Ishikawa, Kazuyoshi; Hirata, Yuji*
JAERI-Tech 2002-074, 22 Pages, 2002/09
The pressurized tube specimens which enclosed high pressure inert gas were produced for the irradiation creep test. The pressurized tube specimen with 7mm outer diameter and 0.5mm wall thickness must be sealed by the welding, after the helium gas was impressed in the inside of tube. In this process, there was a technical problem of welding under high pressure, and it is difficult to seal the pressurized tube specimen in the present facility of our group. The production process was examined by taking shortening in production period and reduction in the cost into consideration. The sealing technology to enclose the helium gas up to 5.5MPa was established by new technique using the present facility and the mock-up test. And, it is necessary to measure the outer diameter of the pressurized tube specimen with high accuracy in order to predict irradiation creep deformation arising from neutron radiation and internal pressure. Therefore, the method for measuring at the 0.01mm measurement accuracy was established, which combined laser measuring instrument with the lathe.
Hatae, Takaki; JT-60 Team
Proceedings of 6th Japan-Australia Workshop on Plasma Diagnostics (CD-ROM), 16 Pages, 2002/00
The diagnostic system of JT-60U is composed of about 50 individual diagnostic devices. Recently, the detailed radial profile measurements of plasma parameters such as electron temperature, electron density, ion temperature, plasma rotation, and plasma current (safety factor q) have been improved. As a result, the understanding of internal structure of plasmas has advanced. In particular, detailed studies of the internal transport barrier could be performed in reversed magnetic shear plasmas. Furthermore, a "current hole" or a nearly zero current density at the plasma center was discovered in JT-60U plasmas by using a motional stark effect (MSE) system. Several diagnostic signal have been linked to actuators such as neutral beam injectors, the gas feed system, and the electron cyclotron heating system establishing the real-time control of electron temperature, neutron yield, radiated power, and electron temperature gradient, and thus improving plasma performance.
Oba, Masaki; Wakaida, Ikuo; Miyabe, Masabumi
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 40(1), p.357 - 358, 2001/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.06(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
 laser in JT-60U
laser in JT-60UKondoh, Takashi; Lee, S.; Hutchinson, D. P.*; Richards, R. K.*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 72(1), p.1143 - 1146, 2001/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:59.37(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
 laser in JT-60U
laser in JT-60UKondoh, Takashi; Lee, S.; Miura, Yukitoshi
Proceedings of 10th International Symposium on Laser-Aided Plasma Diagnostics, p.109 - 114, 2001/00
A collective Thomson scattering (CTS) diagnostic system based on a CO laser has come into operation to establish measurement technique of ion temperature and fast alpha particle in fusion plasmas. A pulsed CO2 laser (wavelength 10.6
laser has come into operation to establish measurement technique of ion temperature and fast alpha particle in fusion plasmas. A pulsed CO2 laser (wavelength 10.6 m, beam energy 15 J, pulse width 1
m, beam energy 15 J, pulse width 1 s) and a heterodyne receiver were developed by Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) and were installed in the JT-60U tokamak. Commissioning of the CTS system by injecting the CO
s) and a heterodyne receiver were developed by Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) and were installed in the JT-60U tokamak. Commissioning of the CTS system by injecting the CO laser into the plasmas has been proceeded.
laser into the plasmas has been proceeded.
Hatae, Takaki; Naito, Osamu
Proceedings of 10th International Symposium on Laser-Aided Plasma Diagnostics, p.160 - 166, 2001/00
In recent strong electron heating experiments in JT-60U, it seems that central 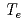 rises above
rises above  15 keV which is measured by Ruby laser and YAG laser Thomson scattering systems. However, error bars are relatively large and it is difficult to measure the very high
15 keV which is measured by Ruby laser and YAG laser Thomson scattering systems. However, error bars are relatively large and it is difficult to measure the very high 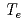 beyond
beyond  15 keV with high accuracy because the electron temperature region exceeds that of the original design. To improve the measurement performance in very high
15 keV with high accuracy because the electron temperature region exceeds that of the original design. To improve the measurement performance in very high 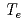 , we have tried the combination of existing Ruby laser system and YAG laser system. From simulations, it was found that (1) changing the form of the spectrum with the other laser is an effective way for very high
, we have tried the combination of existing Ruby laser system and YAG laser system. From simulations, it was found that (1) changing the form of the spectrum with the other laser is an effective way for very high 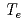 measurement, (2) furthermore the combined system in YAG laser scattering is well optimized at
measurement, (2) furthermore the combined system in YAG laser scattering is well optimized at 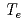
 20keV and relative error is reduced significantly compared with original system.
20keV and relative error is reduced significantly compared with original system.